How Reverse Osmosis Process Works
What Is Osmosis?
Osmosis is a passive process and happens without any additional energy. It involves the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration until the concentrations become equal on either side.
Any solvent can undergo the process of osmosis including gases and supercritical liquids. This is physics that works without any pressure or membranes.
Osmosis process is significant in live organisms such as humans , animals and plants.
Any solvent can undergo the process of osmosis including gases and supercritical liquids. This is physics that works without any pressure or membranes.
Osmosis process is significant in live organisms such as humans , animals and plants.
What Is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a process of pushing water through a material, such as a membrane , primarily used to separate dissolved solutes from water. Reverse osmosis is most commonly known for its use in drinking water purification particularly with regard to removing salt and other contaminants from water.
While water is being pressured through a semi-permeable membrane, it separates water into two flows, clean and "dirty".
While water is being pressured through a semi-permeable membrane, it separates water into two flows, clean and "dirty".
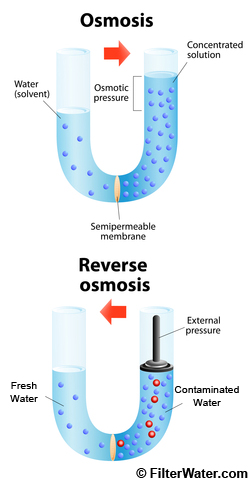
Image courtesy of FilterWater.com
Osmotic Pressure is pressure required to stop water from diffusing through a media such as a membrane.
If you are looking for a residential or commercial water purification system, please contact us here:

